Dental Electricity
Explore the intersection of dental science and electrical technology with "Dental Electricity" by Levitt E. Custer. This historical work delves into the application of electricity in dental practices, revealing early methods and innovations in electrotherapeutics. Discover how electricity was utilized in dentistry, offering a fascinating glimpse into the evolution of medical techniques. A valuable resource for historians of science, dental professionals, and anyone curious about the pioneering uses of technology in medicine.This work has been selected by scholars as being culturally important, and is part of the knowledge base of civilization as we know it. This work was reproduced from the original artifact, and remains as true to the original work as possible. Therefore, you will see the original copyright references, library stamps (as most of these works have been housed in our most important libraries around the world), and other notations in the work.This work is in the public domain in the United States of America, and possibly other nations. Within the United States, you may freely copy and distribute this work, as no entity (individual or corporate) has a copyright on the body of the work.As a reproduction of a historical artifact, this work may contain missing or blurred pages, poor pictures, errant marks, etc. Scholars believe, and we concur, that this work is important enough to be preserved, reproduced, and made generally available to the public. We appreciate your support of the preservation process, and thank you for being an important part of keeping this knowledge alive and relevant.
Dental Materia Medica
"Dental Materia Medica" is a comprehensive resource on the various medicinal substances used in dental practice. This detailed guide, intended for dental students and practitioners, explores the properties, preparation, and application of numerous drugs and compounds relevant to oral health. The book covers a wide array of topics, including antiseptics, analgesics, anesthetics, and other agents used to treat dental ailments and maintain oral hygiene.Organized for easy reference, each entry provides a thorough description of the substance, its source, chemical composition, physiological effects, and therapeutic uses. This classic text offers valuable insights into the traditional methods and materials employed in dentistry, making it an essential addition to any dental professional's library. Whether for historical interest or practical application, "Dental Materia Medica" remains a significant work in the field of dental medicine.This work has been selected by scholars as being culturally important, and is part of the knowledge base of civilization as we know it. This work was reproduced from the original artifact, and remains as true to the original work as possible. Therefore, you will see the original copyright references, library stamps (as most of these works have been housed in our most important libraries around the world), and other notations in the work.This work is in the public domain in the United States of America, and possibly other nations. Within the United States, you may freely copy and distribute this work, as no entity (individual or corporate) has a copyright on the body of the work.As a reproduction of a historical artifact, this work may contain missing or blurred pages, poor pictures, errant marks, etc. Scholars believe, and we concur, that this work is important enough to be preserved, reproduced, and made generally available to the public. We appreciate your support of the preservation process, and thank you for being an important part of keeping this knowledge alive and relevant.
Dental Electricity
Explore the intersection of dental science and electrical technology with "Dental Electricity" by Levitt E. Custer. This historical work delves into the application of electricity in dental practices, revealing early methods and innovations in electrotherapeutics. Discover how electricity was utilized in dentistry, offering a fascinating glimpse into the evolution of medical techniques. A valuable resource for historians of science, dental professionals, and anyone curious about the pioneering uses of technology in medicine.This work has been selected by scholars as being culturally important, and is part of the knowledge base of civilization as we know it. This work was reproduced from the original artifact, and remains as true to the original work as possible. Therefore, you will see the original copyright references, library stamps (as most of these works have been housed in our most important libraries around the world), and other notations in the work.This work is in the public domain in the United States of America, and possibly other nations. Within the United States, you may freely copy and distribute this work, as no entity (individual or corporate) has a copyright on the body of the work.As a reproduction of a historical artifact, this work may contain missing or blurred pages, poor pictures, errant marks, etc. Scholars believe, and we concur, that this work is important enough to be preserved, reproduced, and made generally available to the public. We appreciate your support of the preservation process, and thank you for being an important part of keeping this knowledge alive and relevant.
Dental Materia Medica
"Dental Materia Medica" is a comprehensive resource on the various medicinal substances used in dental practice. This detailed guide, intended for dental students and practitioners, explores the properties, preparation, and application of numerous drugs and compounds relevant to oral health. The book covers a wide array of topics, including antiseptics, analgesics, anesthetics, and other agents used to treat dental ailments and maintain oral hygiene.Organized for easy reference, each entry provides a thorough description of the substance, its source, chemical composition, physiological effects, and therapeutic uses. This classic text offers valuable insights into the traditional methods and materials employed in dentistry, making it an essential addition to any dental professional's library. Whether for historical interest or practical application, "Dental Materia Medica" remains a significant work in the field of dental medicine.This work has been selected by scholars as being culturally important, and is part of the knowledge base of civilization as we know it. This work was reproduced from the original artifact, and remains as true to the original work as possible. Therefore, you will see the original copyright references, library stamps (as most of these works have been housed in our most important libraries around the world), and other notations in the work.This work is in the public domain in the United States of America, and possibly other nations. Within the United States, you may freely copy and distribute this work, as no entity (individual or corporate) has a copyright on the body of the work.As a reproduction of a historical artifact, this work may contain missing or blurred pages, poor pictures, errant marks, etc. Scholars believe, and we concur, that this work is important enough to be preserved, reproduced, and made generally available to the public. We appreciate your support of the preservation process, and thank you for being an important part of keeping this knowledge alive and relevant.
Photobiomodulation Therapy in Oral Medicine
Photobiomodulation (PBM) includes a broad range of nonionizing light sources that, when applied to tissues, lead to anti-inflammatory effects, promote wound healing and tissue repair, improve neural function, and exert an analgesic effect. Although PBM is well established and accessible technique, there is great variability in PBM parameters, protocols, and equipment, which hampers consistent application. This comprehensive book intents to assist the clinician in determining the most appropriate PBM parameters according to the light source available, in a practical and easy way. Written by experts in the PBM and Oral Medicine fields, it provides the utmost protocols for treatment and prevention of the most prevalent diseases and conditions affecting the mouth and the mandibulo-maxillary complex, in the day-to-day patient care. The protocols have been established based on published articles with high scientific evidence, mainly Systematic Reviews, Meta-analysis, and Randomized Clinical Trials. The work is divided into three main sections: Photobiomodulation, Supportive Care in Cancer, and Oral Medicine. In each part, the subtopics encompass the most prevalent and relevant diseases and conditions that may beneficiate of PBM therapy. All chapters include a brief disease definition, followed by diagnosis methods and treatment options including PBM. Each chapter presents a suggestion of PBM protocol, with reproducible parameters that may be easily performed by qualified professionals. Photobiomodulation Therapy in Oral Medicine - Evidence-based Clinical Protocols aims to assist clinical practitioners in decision-making when it comes to classical Oral Medicine, oncology support as well as bone healing and repair.
Advanced Impression Taking
"Advanced Impression Taking: Scientific And Correct Method Based Upon Principles Founded By Drs. Greene" presents a detailed guide to the art and science of taking accurate dental impressions. Authored by Robert H. Lieberthal, this book meticulously outlines the principles and techniques developed by Drs. Greene, offering a scientific approach to achieving precision in dental prosthetics. This book is invaluable for dental students, practicing dentists, and laboratory technicians seeking to refine their skills in impression taking. It emphasizes the importance of a systematic and scientifically grounded methodology for creating dental impressions that are essential for the successful fabrication of dental prostheses. Readers will gain insights into the nuances of the Greene Method, enabling them to enhance the quality and accuracy of their work.This work has been selected by scholars as being culturally important, and is part of the knowledge base of civilization as we know it. This work was reproduced from the original artifact, and remains as true to the original work as possible. Therefore, you will see the original copyright references, library stamps (as most of these works have been housed in our most important libraries around the world), and other notations in the work.This work is in the public domain in the United States of America, and possibly other nations. Within the United States, you may freely copy and distribute this work, as no entity (individual or corporate) has a copyright on the body of the work.As a reproduction of a historical artifact, this work may contain missing or blurred pages, poor pictures, errant marks, etc. Scholars believe, and we concur, that this work is important enough to be preserved, reproduced, and made generally available to the public. We appreciate your support of the preservation process, and thank you for being an important part of keeping this knowledge alive and relevant.
Advanced Impression Taking
"Advanced Impression Taking: Scientific And Correct Method Based Upon Principles Founded By Drs. Greene" presents a detailed guide to the art and science of taking accurate dental impressions. Authored by Robert H. Lieberthal, this book meticulously outlines the principles and techniques developed by Drs. Greene, offering a scientific approach to achieving precision in dental prosthetics. This book is invaluable for dental students, practicing dentists, and laboratory technicians seeking to refine their skills in impression taking. It emphasizes the importance of a systematic and scientifically grounded methodology for creating dental impressions that are essential for the successful fabrication of dental prostheses. Readers will gain insights into the nuances of the Greene Method, enabling them to enhance the quality and accuracy of their work.This work has been selected by scholars as being culturally important, and is part of the knowledge base of civilization as we know it. This work was reproduced from the original artifact, and remains as true to the original work as possible. Therefore, you will see the original copyright references, library stamps (as most of these works have been housed in our most important libraries around the world), and other notations in the work.This work is in the public domain in the United States of America, and possibly other nations. Within the United States, you may freely copy and distribute this work, as no entity (individual or corporate) has a copyright on the body of the work.As a reproduction of a historical artifact, this work may contain missing or blurred pages, poor pictures, errant marks, etc. Scholars believe, and we concur, that this work is important enough to be preserved, reproduced, and made generally available to the public. We appreciate your support of the preservation process, and thank you for being an important part of keeping this knowledge alive and relevant.
A Study Of The Degeneracy Of The Jaws Of The Human Race
"A Study Of The Degeneracy Of The Jaws Of The Human Race" (1892), by Eugene S. Talbot, presents a detailed examination of the changes and deterioration observed in human jaw structures. This work delves into the anatomical and physiological aspects of the jaw, exploring the potential causes and implications of its degeneration. Talbot's research provides valuable insights into the medical and anthropological understanding of the human body during the late 19th century. The book remains a significant resource for those studying the history of dentistry, physical anthropology, and the evolution of human anatomy. This historical text offers a fascinating glimpse into the medical perspectives of the time and the ongoing study of human physical development.This work has been selected by scholars as being culturally important, and is part of the knowledge base of civilization as we know it. This work was reproduced from the original artifact, and remains as true to the original work as possible. Therefore, you will see the original copyright references, library stamps (as most of these works have been housed in our most important libraries around the world), and other notations in the work.This work is in the public domain in the United States of America, and possibly other nations. Within the United States, you may freely copy and distribute this work, as no entity (individual or corporate) has a copyright on the body of the work.As a reproduction of a historical artifact, this work may contain missing or blurred pages, poor pictures, errant marks, etc. Scholars believe, and we concur, that this work is important enough to be preserved, reproduced, and made generally available to the public. We appreciate your support of the preservation process, and thank you for being an important part of keeping this knowledge alive and relevant.
Brother Bill’s Letters And Business Building Articles. Reprinted From ”the Dental Digest” In 1909
Brother Bill's Letters And Business Building Articles, reprinted from "The Dental Digest" in 1909, offers a fascinating glimpse into the world of early 20th-century dental practice and business. Penned with a distinctive voice, these letters and articles provide practical advice and insights on how to build a successful dental business during a period of significant change and growth in the profession.The collection focuses on techniques for attracting and retaining patients, improving communication, and enhancing the overall patient experience. While originally aimed at dentists of the era, the principles discussed retain their value and relevance for anyone interested in understanding the evolution of dental marketing and practice management. This reprint serves as both a valuable historical document and a source of timeless wisdom for business professionals.This work has been selected by scholars as being culturally important, and is part of the knowledge base of civilization as we know it. This work was reproduced from the original artifact, and remains as true to the original work as possible. Therefore, you will see the original copyright references, library stamps (as most of these works have been housed in our most important libraries around the world), and other notations in the work.This work is in the public domain in the United States of America, and possibly other nations. Within the United States, you may freely copy and distribute this work, as no entity (individual or corporate) has a copyright on the body of the work.As a reproduction of a historical artifact, this work may contain missing or blurred pages, poor pictures, errant marks, etc. Scholars believe, and we concur, that this work is important enough to be preserved, reproduced, and made generally available to the public. We appreciate your support of the preservation process, and thank you for being an important part of keeping this knowledge alive and relevant.
Brother Bill’s Letters And Business Building Articles. Reprinted From ”the Dental Digest” In 1909
Brother Bill's Letters And Business Building Articles, reprinted from "The Dental Digest" in 1909, offers a fascinating glimpse into the world of early 20th-century dental practice and business. Penned with a distinctive voice, these letters and articles provide practical advice and insights on how to build a successful dental business during a period of significant change and growth in the profession.The collection focuses on techniques for attracting and retaining patients, improving communication, and enhancing the overall patient experience. While originally aimed at dentists of the era, the principles discussed retain their value and relevance for anyone interested in understanding the evolution of dental marketing and practice management. This reprint serves as both a valuable historical document and a source of timeless wisdom for business professionals.This work has been selected by scholars as being culturally important, and is part of the knowledge base of civilization as we know it. This work was reproduced from the original artifact, and remains as true to the original work as possible. Therefore, you will see the original copyright references, library stamps (as most of these works have been housed in our most important libraries around the world), and other notations in the work.This work is in the public domain in the United States of America, and possibly other nations. Within the United States, you may freely copy and distribute this work, as no entity (individual or corporate) has a copyright on the body of the work.As a reproduction of a historical artifact, this work may contain missing or blurred pages, poor pictures, errant marks, etc. Scholars believe, and we concur, that this work is important enough to be preserved, reproduced, and made generally available to the public. We appreciate your support of the preservation process, and thank you for being an important part of keeping this knowledge alive and relevant.
A Study Of The Degeneracy Of The Jaws Of The Human Race
"A Study Of The Degeneracy Of The Jaws Of The Human Race" (1892), by Eugene S. Talbot, presents a detailed examination of the changes and deterioration observed in human jaw structures. This work delves into the anatomical and physiological aspects of the jaw, exploring the potential causes and implications of its degeneration. Talbot's research provides valuable insights into the medical and anthropological understanding of the human body during the late 19th century. The book remains a significant resource for those studying the history of dentistry, physical anthropology, and the evolution of human anatomy. This historical text offers a fascinating glimpse into the medical perspectives of the time and the ongoing study of human physical development.This work has been selected by scholars as being culturally important, and is part of the knowledge base of civilization as we know it. This work was reproduced from the original artifact, and remains as true to the original work as possible. Therefore, you will see the original copyright references, library stamps (as most of these works have been housed in our most important libraries around the world), and other notations in the work.This work is in the public domain in the United States of America, and possibly other nations. Within the United States, you may freely copy and distribute this work, as no entity (individual or corporate) has a copyright on the body of the work.As a reproduction of a historical artifact, this work may contain missing or blurred pages, poor pictures, errant marks, etc. Scholars believe, and we concur, that this work is important enough to be preserved, reproduced, and made generally available to the public. We appreciate your support of the preservation process, and thank you for being an important part of keeping this knowledge alive and relevant.
Handbook Of Medicine And Therapeutics
The "Handbook of Medicine and Therapeutics" is a comprehensive guide designed for medical professionals and students. This handbook provides a concise overview of essential medical information, covering a wide range of topics from general medicine to specialized therapeutics. Organized for quick reference, it includes key diagnostic criteria, treatment protocols, and management strategies for various medical conditions. Ideal for use in clinical settings, this handbook serves as a valuable resource for making informed decisions and delivering effective patient care. Its practical format and focus on therapeutic interventions make it an indispensable tool for healthcare providers seeking up-to-date and reliable information.This work has been selected by scholars as being culturally important, and is part of the knowledge base of civilization as we know it. This work was reproduced from the original artifact, and remains as true to the original work as possible. Therefore, you will see the original copyright references, library stamps (as most of these works have been housed in our most important libraries around the world), and other notations in the work.This work is in the public domain in the United States of America, and possibly other nations. Within the United States, you may freely copy and distribute this work, as no entity (individual or corporate) has a copyright on the body of the work.As a reproduction of a historical artifact, this work may contain missing or blurred pages, poor pictures, errant marks, etc. Scholars believe, and we concur, that this work is important enough to be preserved, reproduced, and made generally available to the public. We appreciate your support of the preservation process, and thank you for being an important part of keeping this knowledge alive and relevant.
Handbook Of Medicine And Therapeutics
The "Handbook of Medicine and Therapeutics" is a comprehensive guide designed for medical professionals and students. This handbook provides a concise overview of essential medical information, covering a wide range of topics from general medicine to specialized therapeutics. Organized for quick reference, it includes key diagnostic criteria, treatment protocols, and management strategies for various medical conditions. Ideal for use in clinical settings, this handbook serves as a valuable resource for making informed decisions and delivering effective patient care. Its practical format and focus on therapeutic interventions make it an indispensable tool for healthcare providers seeking up-to-date and reliable information.This work has been selected by scholars as being culturally important, and is part of the knowledge base of civilization as we know it. This work was reproduced from the original artifact, and remains as true to the original work as possible. Therefore, you will see the original copyright references, library stamps (as most of these works have been housed in our most important libraries around the world), and other notations in the work.This work is in the public domain in the United States of America, and possibly other nations. Within the United States, you may freely copy and distribute this work, as no entity (individual or corporate) has a copyright on the body of the work.As a reproduction of a historical artifact, this work may contain missing or blurred pages, poor pictures, errant marks, etc. Scholars believe, and we concur, that this work is important enough to be preserved, reproduced, and made generally available to the public. We appreciate your support of the preservation process, and thank you for being an important part of keeping this knowledge alive and relevant.
Dental Caries
"A HAPPY MOUTH IS..... A HAPPY BODY."Shiny teeth brighten your Healthy Smile. Explore the intricate world of dental science and the battle against tooth decay in this comprehensive guide. Delve into prevention, the impact of oral health on overall well-being, and the power of knowledge, illustrated with clarity and backed by extensive research and heartfelt acknowledgments.
Maxillary and Midface Reconstruction, Part 2, an Issue of Atlas of the Oral & Maxillofacial Surgery Clinics
In this issue of Atlas of the Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery Clinics, guest editors Drs. James C. Melville, Rui P. Fernandes, and Michael R. Markiewicz bring their considerable expertise to the topic of Maxillary and Midface Reconstruction, Part 2. This issue is Part 2 of a complete review of reconstruction of the midface and maxilla, featuring articles on reconstructing the orbit, reconstruction of skull base defects, tissue engineering and customized flaps, reconstruction for ballistic and avulsive injuries, pediatric facial reconstruction, and more.Contains 10 relevant, practice-oriented topics including an update on the technological future of reconstruction; consideration and technique in pediatric reconstructions; maxillary and midface reconstruction in non-ideal situations: troubleshooting in a difficult surgical field; and moreProvides in-depth clinical reviews on maxillary and midface reconstruction, offering actionable insights for clinical practicePresents the latest information on this timely, focused topic under the leadership of experienced editors in the field. Authors synthesize and distill the latest research and practice guidelines to create clinically significant, topic-based reviews
On the Relations Which Dental Caries (as Discovered Amongst the Ancient Inhabitants of Britain, and Amongst Existing Aboriginal Races) may be Supposed to Hold to Their Food and Social Condition
In 璽€œOn the Relations Which Dental Caries璽€]璽€, John Rigden Mummery explores the prevalence of dental caries (cavities) in ancient British populations and existing aboriginal races. This historical study delves into the potential connections between dental health, dietary habits, and social circumstances. Mummery's work provides valuable insights into the lives and health of past populations, offering a unique perspective on the interplay between environment, lifestyle, and physical well-being. This text is of interest to historians, anthropologists, and anyone fascinated by the intersection of dental health and social history.This work has been selected by scholars as being culturally important, and is part of the knowledge base of civilization as we know it. This work was reproduced from the original artifact, and remains as true to the original work as possible. Therefore, you will see the original copyright references, library stamps (as most of these works have been housed in our most important libraries around the world), and other notations in the work.This work is in the public domain in the United States of America, and possibly other nations. Within the United States, you may freely copy and distribute this work, as no entity (individual or corporate) has a copyright on the body of the work.As a reproduction of a historical artifact, this work may contain missing or blurred pages, poor pictures, errant marks, etc. Scholars believe, and we concur, that this work is important enough to be preserved, reproduced, and made generally available to the public. We appreciate your support of the preservation process, and thank you for being an important part of keeping this knowledge alive and relevant.
On the Relations Which Dental Caries (as Discovered Amongst the Ancient Inhabitants of Britain, and Amongst Existing Aboriginal Races) may be Supposed to Hold to Their Food and Social Condition
In 璽€œOn the Relations Which Dental Caries璽€]璽€, John Rigden Mummery explores the prevalence of dental caries (cavities) in ancient British populations and existing aboriginal races. This historical study delves into the potential connections between dental health, dietary habits, and social circumstances. Mummery's work provides valuable insights into the lives and health of past populations, offering a unique perspective on the interplay between environment, lifestyle, and physical well-being. This text is of interest to historians, anthropologists, and anyone fascinated by the intersection of dental health and social history.This work has been selected by scholars as being culturally important, and is part of the knowledge base of civilization as we know it. This work was reproduced from the original artifact, and remains as true to the original work as possible. Therefore, you will see the original copyright references, library stamps (as most of these works have been housed in our most important libraries around the world), and other notations in the work.This work is in the public domain in the United States of America, and possibly other nations. Within the United States, you may freely copy and distribute this work, as no entity (individual or corporate) has a copyright on the body of the work.As a reproduction of a historical artifact, this work may contain missing or blurred pages, poor pictures, errant marks, etc. Scholars believe, and we concur, that this work is important enough to be preserved, reproduced, and made generally available to the public. We appreciate your support of the preservation process, and thank you for being an important part of keeping this knowledge alive and relevant.
Tissue Fixation and Processing
This comprehensive manual provides an in-depth exploration of tissue fixation, processing, and embedding techniques essential in histopathology and biomedical research. Beginning with the fundamental concepts of autolysis and fixation, the book delves into the chemistry and classification of various fixatives including aldehydes, oxidizing agents, protein denaturants, and cross-linking compounds highlighting their mechanisms, applications, and impact on tissue morphology and staining properties. It further addresses the physical and chemical factors affecting fixation, such as pH, temperature, penetration rate, and osmolality. Detailed discussions cover both conventional and advanced methods like microwave fixation and the use of secondary fixatives for enhanced preservation. The book also provides extensive guidance on tissue processing stages, including dehydration, clearing, impregnation, and embedding using paraffin, celloidin, resins, and ester wax. Special sections include techniques for photomicrography, image analysis, and tumor marker identification, offering valuable insights for diagnostic and research applications.
Microvascular Reconstruction in Head and Neck
The deformities of the head or neck are often the result of trauma, oncologic resection, infection, osteoradionecrosis, and congenital or developmental pathology. Multiple tissue types that compose the craniofacial region including bone, cartilage, nerve, fat, muscle, mucosa, and varying dermal and epidermal thickness, as well the inherently intricate contours of the craniofacial skeleton can complicate reconstruction. The introduction and refinement of free tissue transfer (FTT), combined with microvascular anastomosis, allows major ablative defects to be reliably reconstructed with a single operation, undertaken at resection. FTT success rates ranging from 94.3% to 99% have generally been reported. However, as with any surgical procedure, local, general, and specific complications can be encountered in the perioperative period.However, significant advances in microvascular and craniomaxillofacial surgery over the past 50 years have resulted in dramatically improved outcomes. This book throws a light on the various techniques and flaps used in head and neck reconstruction.
Immunotherapy in Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma
Immunotherapy has emerged as a promising modality in the treatment of Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma (OSCC), particularly for advanced and recurrent cases. Unlike conventional therapies, which target the tumor directly, immunotherapy harnesses the body's immune system to recognize and destroy cancer cells. The most widely studied approach in OSCC involves immune checkpoint inhibitors targeting the PD-1/PD-L1 axis. Drugs like nivolumab and pembrolizumab have demonstrated improved survival rates in patients with recurrent or metastatic OSCC, especially those with PD-L1 expression.Combining immunotherapy with surgery, radiotherapy, or chemotherapy is being explored to increase efficacy. As research progresses, personalized immunotherapy guided by molecular profiling holds the potential to significantly improve prognosis and quality of life for OSCC patients. Continuous clinical trials and translational research are critical to overcoming current limitations and expanding its therapeutic role.
Minimally Invasive Endodontic Access Cavities
Whereas traditional access cavities are portrayed as a dentist-conveniencefocused treatment, minimal access cavity preparation has been advocated as a patientcentered clinical strategy. The argument seems convincing at first glance because the old method is based on standardised shapes to provide direct access to all canal orifices, whereas dentine conservation through minimal cavities is intended to be achieved according to the clinical situations of teeth. The main justification for the socalled patient-centered approach is that the minimally invasive concept typically promotes the significance of leaving as much of the pulp chamber roof intact as possible. This is supported by the hypothesis that this is relevant to maintaining the overall resistance strength of teeth and, consequently, their long-term survival.
Biomimetic Materials in Dentistry
Biomimetic Materials in DentistryBiomimetic materials mimic natural dental tissues. Key materials include hydroxyapatite (HA), which promotes remineralization, and alumina ceramics, known for fracture resistance.AdvantagesTooth Preservation: Minimizes tooth preparation, maintaining tooth integrity.Durability: Longer-lasting, more resistant to fractures.Aesthetics: Closely matches natural tooth color and translucency.Biocompatibility: Reduces adverse reactions, supports oral health.TechniquesAdhesive Restorations: Bond directly to teeth, minimizing preparation.Biomimetic Coatings: Enhance implant integration and tissue regeneration.Tissue Engineering: Uses enamel matrix derivatives to regenerate tissues.Challenges & Future DirectionsChallenges include fully replicating natural tooth properties. Future research may focus on self-healing materials, improved bonding, and better tissue regeneration.ConclusionBiomimetic dentistry promotes minimally invasive, patient-centered care, with promising advancements for the future of dental treatments.
Extraction of the Mandibular Third Molar
This book is a comprehensive and evidence-based guide to the extraction of the mandibular third molar tooth. It includes sophisticated anatomical and radiological images, discusses contemporary scientific data based on the latest research, and guides the reader through the examination process and the surgical techniques of the extraction. The book is divided into five sections. In the first two sections, readers will learn about the basics of the mandibular third molar and the evidence of surgical complications including hemorrhage, pseudoaneurysm, nerve block and nerve injuries. Section 3 and 4 cover surgical techniques and preoperative evaluation such as risk assessment, preoperative conditions, anesthesia, and suturing methods. The last section focusses on clinical case presentations illustrating the management of various patients. This book is a must have for all general dentists, periodontists, specialists and residents of oral surgery, as well as for dental students.
Systemic Factors Affecting Prognosis and Outcomes of Dental Treatment, an Issue of Dental Clinics of North America
In this issue of Dental Clinics, guest editor Dr. Davis Thomas brings his considerable expertise to the topic of Systemic Factors Affecting Prognosis in Dentistry. Many health conditions and diseases can affect oral health, either systemically or due to physical inability to maintain appropriate oral hygiene. Conditions such as chronic pain, stress, or infections present a number of symptoms that may provide challenges to the dentist. This issue takes a holistic approach to treatment planning for systemic factors, with articles on implants, periodontal therapy, medications, genetics, orthodontics, and psychological issues.Contains 15 relevant, practice-oriented topics including systemic factors affecting prognosis of dental implants; COVID-19 and other emerging infections; genetics affecting prognosis of dental treatments; systemic factors affecting prognosis of pain management in dentistry; medications affecting treatment outcomes in dentistry; and more.Provides in-depth clinical reviews on systemic factors affecting prognosis in dentistry, offering actionable insights for clinical practice.Presents the latest information on this timely, focused topic under the leadership of experienced editors in the field. Authors synthesize and distill the latest research and practice guidelines to create clinically significant, topic-based reviews.
Dental Implantology and Bone Reconstruction in Oral Surgery
Dental implantology and bone reconstruction are critical components of modern oral surgery, aimed at restoring function and aesthetics in patients with missing teeth or insufficient jawbone. Dental implants serve as artificial tooth roots, providing a stable foundation for prosthetic restorations such as crowns or bridges. However, successful implantation often requires sufficient bone volume and density, which may be compromised due to trauma, infection, or long-term tooth loss. Bone reconstruction techniques-such as bone grafting, guided bone regeneration, and sinus lift procedures-are employed to rebuild and strengthen the jawbone prior to or during implant placement. Advances in biomaterials and surgical techniques have significantly improved outcomes, allowing for predictable and long-lasting results. By integrating implantology with bone regeneration, oral surgeons can offer comprehensive treatment plans that enhance oral function, facial structure, and patient confidence. This combined approach reflects a growing emphasis on precision, personalization, and long-term success in oral healthcare.
Problem Based Learning .MCQs.
Problem-based learning- Multiple-choice questions(PBL, MCQ) have clinical relevance. They stimulate real-world applied scenarios. They require critical thinking and decision skills similar to those needed in actual patient care. In the world of normal periodontium, we designed questions to be applicable. They allow students or clinicians to apply their knowledge to practical situations they might encounter in practice. They integrate knowledge in the context of anatomy, histology, and physiology. On the other hand, they force learners to prioritize actions. They help learners apply the guidance for assessment, diagnosis, and treatment. They effectively assess and bridge the gap between theory and practice when applied. This book is the first part of a series that addresses this issue. Keywords: Problem-based learning, Multiple-choice questions, Normal periodontium
DNA profiling advances in forensic odontology
DNA profiling, a forensic technique plays a crucial role in forensic odontology. DNA is unique to each individual, making it a highly reliable source for identification especially when identifying individuals from skeletal remains or damaged tissues. Teeth, due to their resilience and hard tissue structure, serve as an excellent source of DNA, making then valuable in investigations. DNA profiling allows for accurate identification, matching antemortem records with post mortem samples and can even provide information on ancestry and sex determination.
Digital Treatment Planning in Dentistry
This work explores the integration of digital technologies in modern dental practices to enhance treatment planning, execution, and patient care. It covers the evolution of digital dentistry, including CAD/CAM systems, 3D printing, artificial intelligence, augmented reality, and teledentistry. The study discusses various digital tools such as intraoral scanners, cone beam computed tomography (CBCT), and digital smile designing for improved diagnosis and treatment visualization. The document also highlights advancements in implant planning, regenerative dentistry, and robotic applications, emphasizing the benefits of precision, efficiency, and patient education. The book concludes that digital workflows have revolutionized prosthodontics, offering better predictability, accuracy, and patient outcomes in treatment procedures.
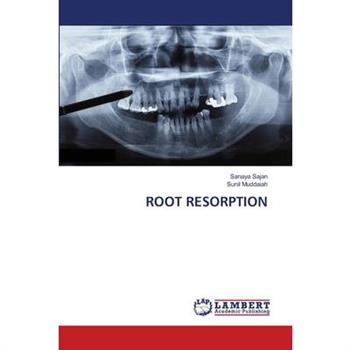
Root Resorption
Root resorption is the most common undesirable effect following the orthodontic treatment. Most common type of root resorption occurring due to orthodontic treatment is external apical root resorption.this book is aimed at providing the reader with comprehensive knowledge of root resorption occurring due to orthodontic treatment, so that at the end of this reading one becomes aware of various factors that lead to resorption and have a better knowledge on how to minimize it.
Implant in Esthetic Zone
Implant in the esthetic zone refers to a dental implant placed in the visible area of the smile, typically front teeth, were achieving a natural aesthetic appearance is crucial due to high visibility when someone smiles; this area requires careful consideration of implant positioning and soft tissue management to achieve optimal esthetic results. Attainment of an aesthetically acceptable final result is central to achieve a successful esthetic result and good patient satisfaction, implant placement in the esthetic zone demands a thorough under-standing of anatomic, biologic, surgical, and prosthetic principle. Ability to achieve harmonious, indistinguishable prosthesis from adjacent natural teeth in esthetic zone is sometimes challenging. Placement of implants in the esthetic zone is a technique-sensitive procedure with little room for error. Guidelines are presented for ideal implant positioning and for a variety of therapeutic modalities that can be implemented for addressing different clinical situations involving replacement of missing teeth in esthetic zone. Addressing these challenges necessitates meticulous treatment planning, effective soft tissue management, follow ups.
Articulators
Articulators are mechanical instruments that represent the maxilla, mandible and TMJs. Their main task is to provide a frame where it is possible to relate, in the three planes of space, the maxillary cast with the mandibular cast relative to the hinge axis of the patient and of the instrument. An articulator serves as a patient in the absence of the patient because it can be programmed with patient records that allows the operator to fabricate a restoration that will be physiologically and psychologically successful.
Bioactive Revolution in Pediatric Dentistry
Bioactive materials in pediatric dentistry interact with biological tissues, release beneficial ions, and promote remineralization, making them valuable for preventing and treating dental caries in children. These materials release calcium, phosphate, and fluoride ions, enhancing tooth repair and protection. Common bioactive materials include glass ionomer cement (GIC), resin-modified GIC, calcium silicate-based cements (e.g., MTA, Biodentine), bioceramic sealers, and hydroxyapatite-based materials. They offer advantages like fluoride release, remineralization, biocompatibility, antimicrobial properties, and long-term durability. They are used in preventive and restorative treatments, including fissure sealants, cavity restorations, pulp therapy, and endodontic procedures. Despite challenges like cost, handling complexity, and esthetic concerns, advancements in nanotechnology and biomaterials are improving their properties. Smart bioactive materials that respond dynamically to oral conditions are under development, ensuring better outcomes in pediatric dental care.
Odontogenic Cyst and Tumors
This comprehensive book focuses on the diagnosis, classification, and management of odontogenic cysts and tumors in children and adolescents. It covers the unique characteristics of these lesions in the pediatric population, including clinical presentation, radiographic features, histopathology, and treatment protocols. The book integrates current research with clinical case studies, making it a valuable resource for pediatric dentists, oral surgeons, and dental students.
The Role of Cytokines in Periodontology
This book explores the pivotal role of cytokines in periodontal health, disease, and healing. Cytokines are small signaling proteins that regulate cellular communication, immune responses, and tissue remodeling. In health, they maintain homeostasis by coordinating cell growth, differentiation, and matrix synthesis. In inflammation, cytokines like IL-1, IL-6, TNF-α, and IL-17 contribute to tissue destruction and bone resorption. The book discusses their mechanisms, receptors, classification, and involvement in immune modulation, chemotaxis, and wound healing. It also highlights anti-inflammatory cytokines such as IL-10 and TGF-β in repair processes, and examines cytokine storms and their systemic implications. Therapeutic strategies targeting cytokines are explored as potential adjuncts in periodontal treatment. With extensive literature support, this book provides a comprehensive understanding of cytokines as key mediators in periodontology.
Anticariogenic Agents Alternative to Fluorides
This book depicts the use of various anticariogenic agents used instead of fluorides. Dental caries is a complex disease process that afflicts a large population of the world, regardless of gender, age and ethnicity, although it does tend to affect more with a low socioeconomic status to a greater extent. New and emerging methods have been and are in the process of being developed. These hold great promise of preventing and reversing caries, especially in the one-fifth of the population that accounts for two thirds of the caries experience. However, despite the dramatic reduction in dental caries rates over the past half century and the concurrent increase in emphasis on preventive dentistry, caries still affects a major percentage of the population. Thus, control of caries is of major importance in dentistry and will continue to be for the foreseeable future.
Tracheostomy
In today's world, tracheostomy is a time-honored procedure, used for managing the airway in acute settings, such as maxillofacial and laryngeal trauma, and establishing a secure airway to manage head and neck infections. Tracheostomy is routinely performed in the intensive care unit for patients on prolonged mechanical ventilation and in the management of head and neck oncological surgeries and reconstruction. The oral and maxillofacial surgeon is routinely involved with surgical procedures requiring a secure airway, acutely, or in the setting of long-term management of the airway.
Artificial Intelligence in Dentistry
Artificial Intelligence (AI) is rapidly transforming the field of dentistry, introducing innovative tools that enhance diagnostic accuracy, treatment planning, and clinical outcomes. The most commonly applied AI technologies in dentistry are artificial neural networks (ANNs) and convolutional neural networks (CNNs), particularly in dental radiology where they support the identification of pathologies and treatment forecasting.AI applications span across various dental specialties. In restorative dentistry, AI detects tooth decay, existing restorations, and supports caries excavation decisions. In endodontics, it assists in identifying periapical lesions, root fractures, and analyzing the root canal system, as well as predicting treatment success and evaluating stem cell viability. Orthodontics benefits from AI in cephalometric analysis, growth assessment, and outcome evaluation, while dental surgery uses AI for orthognathic planning, complication prediction, and implantology. In periodontology, AI aids in monitoring bone loss and predicting periodontitis progression.
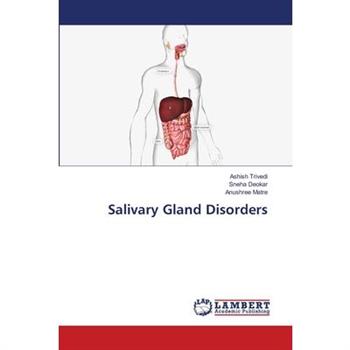
Salivary Gland Disorders
This book describes that the oral cavity is a moist environment; a film of fluid called saliva constantly coats its inner surfaces and occupies the space between the lining oral mucosa and the teeth. Salivary function provides host protection, assists in the initiation of food and fluid intake, and enables communication through speech. Without adequate salivary output, oral and pharyngeal health declines along with a person's quality of life. Salivary dysfunction, however, is not a normal consequence of growing older, and is due to systemic diseases, medications, and head and neck radiotherapy. While complains of xerostomia may be indicative of salivary gland disorder, salivary diseases can present without symptoms. Therefore, routine examination of salivary function must be part of any head, neck and oral examination. Health care professionals can play a vital role in identifying patients at risk for developing salivary dysfunction and should provide appropriate preventive and interceptive techniques that will help preserve a person's health, function, and quality of life.
Antimicrobials in Dentistry
The development and use of antibiotics were one of the most important discoveries of the 20th century, revolutionizing the treatment of infectious diseases, thus saving millions of lives and enabling critical advances in many medical fields. An antibiotic is defined as "a substance produced by microorganisms that can act on other microorganisms (or living cells) by inhibiting their growth or destroying them (antibiotic action)". Indeed, the term, coming from the Greek and meaning "against life", is thus used to refer to drugs that can inhibit or slow down the multiplication of bacteria, either by inhibiting one or more specific metabolic pathways essential to the bacterium or by acting on a specific target of the bacterial cell.
Dental Fluorosis
Fluoride has always been called a double edged sword. On one hand it serves to protect teeth against dental caries and on the other hand it can cause dental fluorosis if consumed in excess.. Due to the increased use of fluoride in preventive dentistry, the prevalence of mild to moderate dental fluorosis is rising in many countries. Dental fluorosis is a condition caused by excessive fluoride intake during enamel formation, leading to discoloration and surface irregularities of the teeth. Management depends on the severity of the condition. This book covers all the new managing strategies for different levels for dental fluorosis.
Matrix Metalloproteinases in Health and Disease
Matrix metalloproteinases (MMPs) have emerged as pivotal enzymes in the regulation of extracellular matrix (ECM) remodeling, orchestrating a wide range of physiological and pathological processes. These zinc-dependent endopeptidases are central to tissue development, wound healing, angiogenesis, and immune responses, while also playing critical roles in pathological conditions such as cancer, cardiovascular disease, arthritis, neurodegeneration, and periodontal disease. As gatekeepers of ECM turnover and modulators of cellular behavior, MMPs have attracted significant attention from researchers and clinicians across the spectrum of biomedical science.Matrix Metalloproteinases in Health and Disease offers a comprehensive, up-to-date exploration of the biology, function, and clinical significance of this powerful enzyme family. This book brings together a multidisciplinary perspective, presenting an integrated view of MMPs from molecular mechanisms to translational applications.
Pulp Therapy of Young Permanent Tooth
Pulp therapy in young permanent teeth is essential in pediatric dentistry to preserve pulp vitality and tooth function after caries or trauma. These teeth often have incompletely developed roots and open apices, requiring tailored treatment to ensure continued root development or closure. Treatment options vary based on pulp status and include indirect and direct pulp capping, pulpotomy, apexogenesis, apexification, and regenerative endodontic procedures. Vital pulp therapies are used for reversible pulpitis, while non-vital therapies are suited for necrotic pulp. Advances in bioactive materials like MTA and biodentine have enhanced healing and dentin bridge formation. Accurate diagnosis, case selection, and follow-up are key for success. Early management ensures long-term tooth retention and supports facial and jaw development.
Fluid Dynamics in Endodontics
*A Scientific Approach to Irrigation Efficiency and Endodontic Success* Fluid Dynamics in Endodontics presents a comprehensive analysis of fluid behavior within the root canal system, integrating principles of physics, bioengineering, and clinical endodontics. This book examines how irrigation solutions interact with the intricate anatomy of root canals, highlighting the importance of flow patterns, shear stress, and turbulence in effective disinfection and debris removal. Ideal for clinicians, researchers, and postgraduate students, it offers evidence-based insights into optimizing irrigation techniques and technologies for enhanced treatment outcomes.
Laser and Its Application in Oral Medicine
Lasers (Light Amplification by Stimulated Emission of Radiation) are advanced tools used in oral medicine for both diagnostic and therapeutic purposes. They offer benefits such as precision, minimal bleeding, reduced pain, and faster healing. Common applications in oral medicine include the treatment of aphthous ulcers, oral lichen planus, leukoplakia, and fibromas. Lasers are also used in biopsy procedures, depigmentation, and photobiomodulation therapy for pain and inflammation control. Their minimally invasive nature makes them a valuable adjunct in modern dental and oral healthcare.
The Evolution of the Smile
The Evolution of the Smile: From Survival to Significance explores the smile's transformation from a primal survival tool to a powerful cultural symbol. Tracing its roots through evolutionary biology, the book examines how facial muscles, neural pathways, and dental changes shaped human expression. Teeth, central to this evolution, adapted with diet and influenced the social smile. Beyond biology, the meaning of smiling varies across cultures-signaling warmth, masking discomfort, or conveying status. The book delves into the psychology behind smiling, its impact on brain chemistry, and its role in empathy. It also reveals ancient dental practices and today's digital enhancements, questioning authenticity in a curated age. This interdisciplinary journey uncovers how smiling reflects emotion, identity, and our shared humanity.
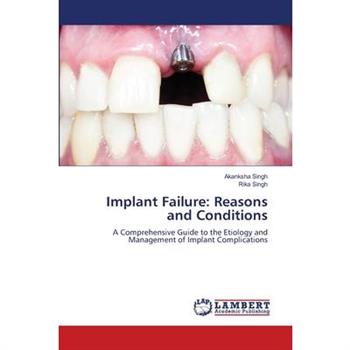
Implant Failure
Implant Failure: Reasons and ConditionsDental implants are one of the most successful and widely adopted treatment modalities in modern dentistry, boasting high long-term survival rates. Yet despite decades of progress in surgical techniques, biomaterials, and prosthetic design, implant failure continues to be a significant clinical challenge. When an implant fails-whether early in the healing phase or years after placement-it carries not only biological and mechanical consequences but also emotional, functional, and financial implications for patients and clinicians alike.Implant Failure: Reasons and Conditions offers a comprehensive and evidence-based exploration of the complex factors that contribute to the failure of dental implants. Bridging foundational science with clinical application, this book brings clarity to the multifactorial nature of implant complications, enabling readers to better understand, diagnose, prevent, and manage failures in practice.Written by specialists in periodontology, this resource dives deep into the biological, mechanical, systemic, and iatrogenic reasons that underlie implant failure.
Anterior Crowns in Pediatric Dentistry
Maintaining a healthy oral cavity is key to good appearance, but dental caries remain the most common chronic disease in children. Primary incisors, vital until permanent teeth emerge, often require restoration to preserve function and aesthetics. Pediatric dentists face challenges in restoring teeth affected by early childhood caries (ECC), balancing factors like tooth structure, moisture control, cooperation, aesthetics, and cost to meet high parental expectations with durable, reliable solutions and a comprehensive understanding of different crown forms. This book provides a concise overview of the various anterior crown types introduced in Pediatric Dentistry, spanning from historical designs to the most recent advancements. It details the techniques for their placement, as well as their indications, contraindications, advantages, and disadvantages. The aim is to assist clinicians in choosing the most suitable crown form for restoring a child's primary anterior teeth, ultimately helping to recreate a healthy, radiant smile.
Basics of Basal and Zygomatic Implants
The dental system plays a crucial role in maintaining masticatory function and nutrient intake. Tooth loss is a common issue, particularly in elderly patients, who require restoration of function and esthetics. Modern dentistry aims to restore normal contour, function, comfort, esthetics, and speech, regardless of the atrophy or disease of the stomatognathic system. Implantology, a branch of dentistry, focuses on rehabilitating edentulous ridges with osseo integrated implants that support prosthetic teeth. Endosseous dental implants are divided into two types: axially inserted crestal implants and laterally inserted basal implants.Conventional crestal implants are inserted into the jaw bone from the crestal alveoli axially, providing good support for prosthesis when adequate bone height and width are present. However, they are expensive, require complex surgical procedures, and can cause complications like screw slackening and fractures.Basal implantology, also known as bicortical implantology, is a modern implantology system that engages the basal cortical bone of both jaws for implant retention.